Link Your Host Name with the LB Domain Name
With traffic control, dynamic name resolution is provided with respect to LB domain names. An LB domain name has format of "lb.example.e.d-16.jp," for example. It is different from your host name.
To change the name resolution result of your host name dynamically, you need to link the LB domain name with your host name.
There are several ways to do so. Select an optimum approach according to your utilization form. Even if you use a service other than the IIJ Managed DNS Service as the authority DNS Server for your host name, you can link he LB domain name with your host name.
[ Reference ]
- If you use a service other than the IIJ Managed DNS Service, you cannot configure the settings with the use of ANAME.
- Use of the LB domain name without linking it to your host name is not recommended.
The LB domain name assigned to you can be checked from "Contract Information" of traffic control.
The following sections use "host.example.jp" as your host name and "lb.example.e.d-16.jp" as the LB domain name.
Linking through the Use of CNAME
Set the LB domain name as CNAME for your domain name.
If you use the "example.jp" zone with the Managed DNS Service, add the following record from "Record Management."
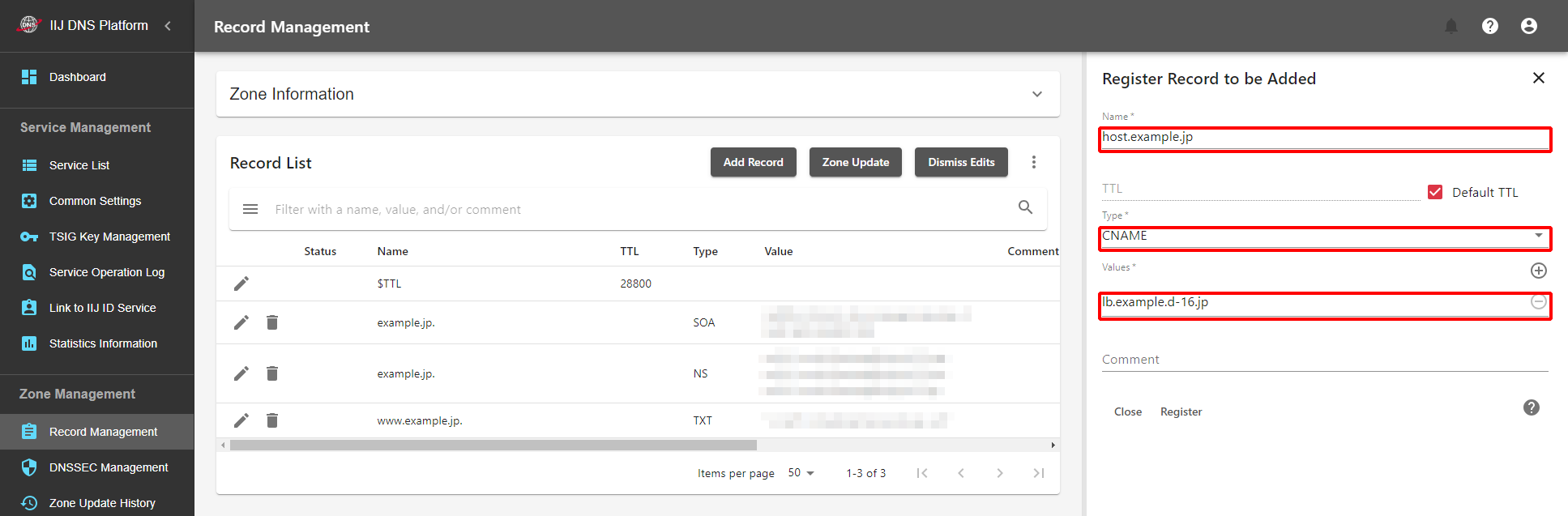
If you conduct the operation with a service other than this service, set the following CNAME to the "example.jp" zone.
host.example.jp. IN CNAME lb.example.e.d-16.jp.
[ Reference ]
The methods using CNAME cannot be used in the following cases.
- When other records already exist in host.example.jp
- If "host.example.jp" exists in the "host.example.jp" zone (at the zone apex) instead of in the "example.jp" zone, the methods using CNAME cannot be used when SOA and NS records already exist.
- When using CNAME in a case where the use of CNAME is not allowed because of the specifications of the protocol such as SMTP
Linking through the Use of ANAME
ANAME is an extended record type unique to the IIJ Managed DNS Service and allows users to make the specification using a host name, such as CNAME, even at the zone apex. Add a record like the one shown below from "Record Management."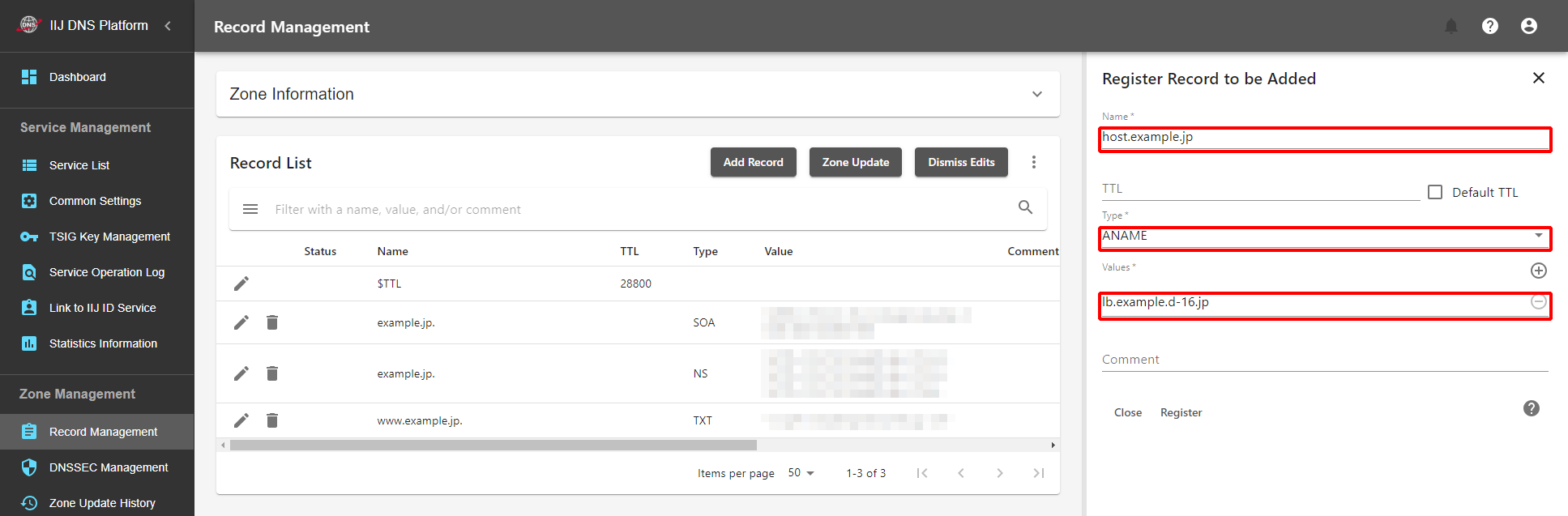
[ Reference ]
The following restrictions apply to how to use ANAME.
- ANAME is an extended function unique to the IIJ Managed DNS Service. It cannot be used when you use the primary DNS server for the "host.example.jp" zone with a service other than this service. Even when you use this service, you cannot use your server as the primary server and this service as the secondary server.
- ANAME can be used only at the zone apex (with the record name which is the same as the zone name). To set ANAME to "host.example.jp," you need to sign up for the "host.example.jp" zone instead of the "example.jp" for the Managed DNS Service. Use other methods such as CNAME for other than the zone apex.
- Response details of ANAME records are not dynamic but are updated at regular time intervals. Fixed response is returned until they are updated next. For this reason, you may not have the desired operation for usage such as load balancing.
Other authority DNS service operators may also provide a unique extended function. For details of how to use the function, contact your business operator. IIJ cannot provide any support.
Linking with the Use of MX/SRV/HTTPS/SVCB
When you use traffic control with a protocol for referencing a specific record type, link your host name with the LB domain name by using each of the record types: MX, SRV, HTTPS, and SVCB.
MX Record
For the usage with the email server, specify the LB domain name for the MX record.
host.example.jp. IN MX 10 lb.example.e.d-16.jp.
[ Reference ]
For the usage as MX, use "entry_a" or "entry_aaaa" (or both) instead of "entry_cname" as the entry method to be specified in "Rule Management." Because "entry_cname" responds to CNAME eventually, the use of it is not suitable for use of MX for which the use of CNAME is prohibited.
SRV Record
For the usage for using SRV records such as SIP, specify the LB domain name as shown below.
_foo._tcp.host.example.jp. IN SRV 1 0 9999 lb.example.e.d-16.jp.
SRV records can also be used together with CNAME as shown below.
_foo._tcp.host.example.jp. IN SRV 1 0 9999 host.example.jp. host.example.jp. IN CNAME lb.example.e.d-16.jp.
HTTPS Record
HTTPS record is a DNS record type to be used for accessing by HTTP(S). To specify the LB domain name using an HTTPS record, configure the setting as shown below.
host.example.jp. IN HTTPS 0 lb.example.e.d-16.jp.
[ Note ]
As of 2022, HTTPS records are not ubiquitous yet; therefore, web browsers that support HTTPS records are limited. For this reason, it is recommended that you use HTTPS records together with other methods when linking the LB domain name and your host name. The method for linking the LB domain name and your host name using HTTPS records only is not recommended at this point.
When you operate the "host.example.jp" zone with the Managed DNS Service, you can use HTTPS records and ANAME records together.
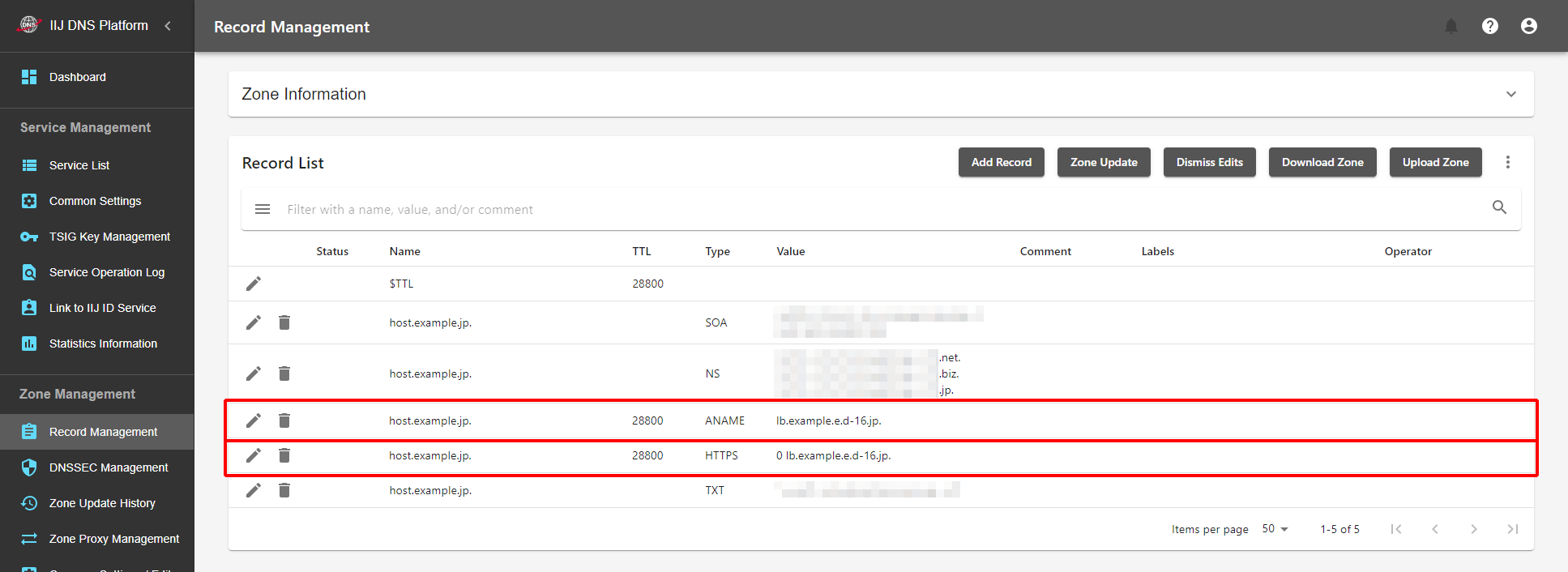
If you configure the setting as shown above, while the client that supports HTTPS records follows the HTTPS record, the client who does not support HTTPS records accesses the LB domain name using the ANAME function.
ANAME can be used only at the zone apex. Therefore, use CNAME instead for the use in a situation other than at the zone apex (in this case, CNAME cannot be used with HTTPS records).
SVCB Record
SVCB record is a general-purpose record type that does not rely on a specific protocol. However, there are no protocols that use SVCB records as of 2022. If you need to specify an SVCB record, do so as shown below.
; For an URL "foo://host.example.jp:9999/" _9999._foo.host.example.jp. IN SVCB 0 lb.example.e.d-16.jp.
Using the LB Domain Name
Use of the LB domain name without linking it to your host name is not recommended.
[ Note ]
Do not create a website that uses the LB domain name as it is (https://lb.example.e.d-16.jp/). There may be security issues, such as a leak of cookies to a website using another LB domain name.